Current Trend in Government Health Spending
Dr. Nawa Raj Subba
Global
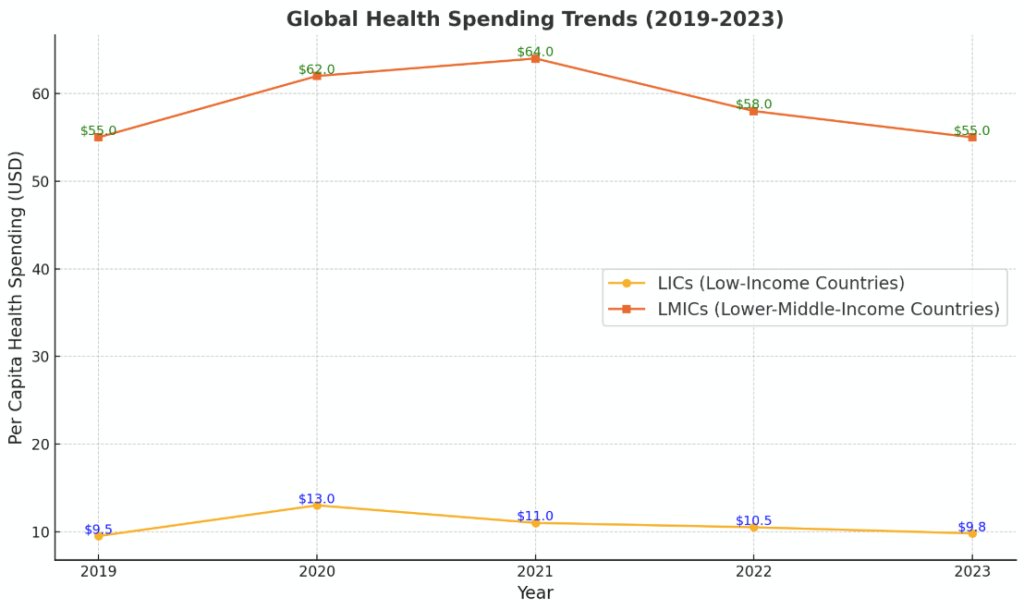
Government health spending in low- and lower-middle-income countries (LICs and LMICs) peaked during the COVID-19 pandemic but has since consistently fallen until 2023, returning to pre-pandemic levels. Per capita spending in LICs rose to $13 in 2020 but decreased to below $10 by 2023. In LMICs, spending increased to $64 in 2021 before falling to $55, near 2019 levels. This drop has reduced annual growth in health investments to only 1.2% between 2019 and 2023, compared to 4.2% in LICs and 2.4% in LMICs from 2015 to 2019. A declining share of government resources allocated to health has reversed previous advances in health prioritization, leaving many nations unable to meet the minimum spending levels required to accomplish the 2030 health-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In 35 nations with a population of more than 2.5 billion, both per capita health spending and the health share of government budgets have fallen.
Nepal
Nepal’s government health spending trends are consistent with the issues faced by other low-income countries (LICs); however, per capita data are context-specific. Nepal’s healthcare spending increased dramatically during the COVID-19 pandemic, with the government dedicating significant resources to tackle the situation. However, like in many LICs, health spending per capita has since decreased, returning to pre-pandemic levels. Globally, LICs peaked at $13 per capita in 2020 but fell to $10 by 2023 (World Bank, 2023). Nepal’s government health spending in 2020 was around $11 per capita, slightly lower than the LIC average (Ministry of Health and Population Nepal, 2021). This reflects a global trend of decreasing health prioritization in budgets following the epidemic, creating considerable obstacles to meeting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030.
Conclusion
Addressing this dilemma demands immediate action to prioritize health spending, increase efficiency, and navigate fiscal constraints, or face setbacks in human growth, poverty reduction, and pandemic readiness.To avoid obstacles in human capital development and poverty reduction, Nepal must urgently prioritize health in its budget while improving spending efficiency and resolving fiscal constraints.
Bibliography
World Bank. (2023). Health spending trends through 2023: Peaks, declines, and mounting risks. Washington, DC: World Bank Group.
Ministry of Health and Population Nepal. (2021). *Annual health report*. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal.